The Evolution of Prosthetics
Prosthetic limbs have a long and rich history that dates back to ancient times. The earliest known prosthetic was found in Egypt and dates back to around 1000 BC. It was an artificial toe made of wood and leather, designed to replace a missing toe in the foot.
Since then, prosthetics have come a long way, with numerous advancements being made in both the design and functionality of these devices. One major milestone in the evolution of prosthetics occurred during World War II when there was an increase in demand for limb replacements due to the high number of soldiers who suffered amputations on the battlefield.
This led to significant advancements in prosthetic technology, with more attention being given to creating devices that were both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Over time, different materials have been used to make prosthetics more durable and lightweight.
For example, wood was commonly used for many centuries until metal became popular in the mid-19th century. In recent years, carbon fiber has become a popular material due to its strength and flexibility.
The Importance of Prosthetics
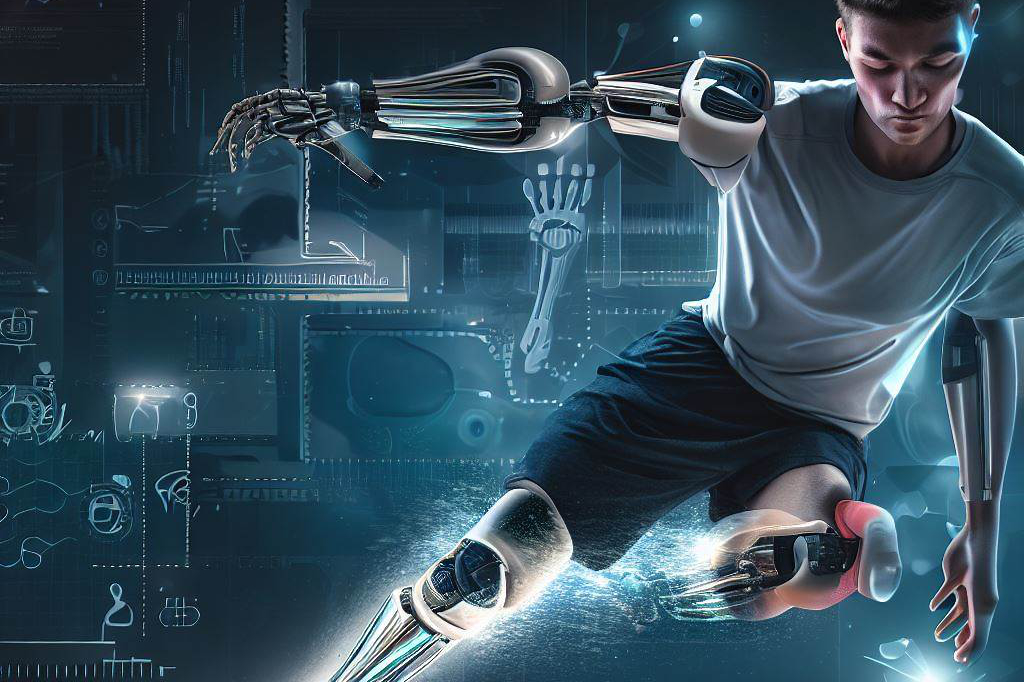

Prosthetics play a crucial role in improving the quality of life for people who have suffered limb loss or impairment. These devices can help restore normal movement patterns, allow individuals to perform daily activities independently, and even allow them to participate in sports or other physical activities.
For children with limb differences, prosthetics can help them fully engage with their peers by providing them with opportunities for play and exploration that would be difficult or impossible without these devices. In addition, prosthetics can help prevent secondary health complications such as joint pain or muscle weakness that may arise from relying on non-prosthetic aids like crutches or wheelchairs.
Prosthetic technology is constantly evolving as manufacturers strive to create devices that are more comfortable, efficient, and effective at restoring function lost through amputation or injury. As a result, people with limb loss today have access to an array of high-tech prosthetic devices that can be customized to suit their unique needs and preferences.
Bionic Limbs
Definition and Explanation of Bionic Limbs
Bionic limbs are prosthetic devices that are designed to replicate the function and appearance of natural limbs. Unlike traditional prosthetics that rely on physical supports and basic mechanisms such as hinges, bionic limbs are integrated with advanced microprocessors, sensors, and motors that enable them to mimic the movement and control of a real limb. The idea of bionic limbs is not entirely new.
In fact, the concept dates back to the 1970s, when researchers began exploring ways to use computer technology in prosthetic design. However, it was not until recent years that advancements in electronics, materials science, and artificial intelligence have made it possible to create truly functional bionic limbs.
Advancements in Technology that Have Made Bionic Limbs Possible
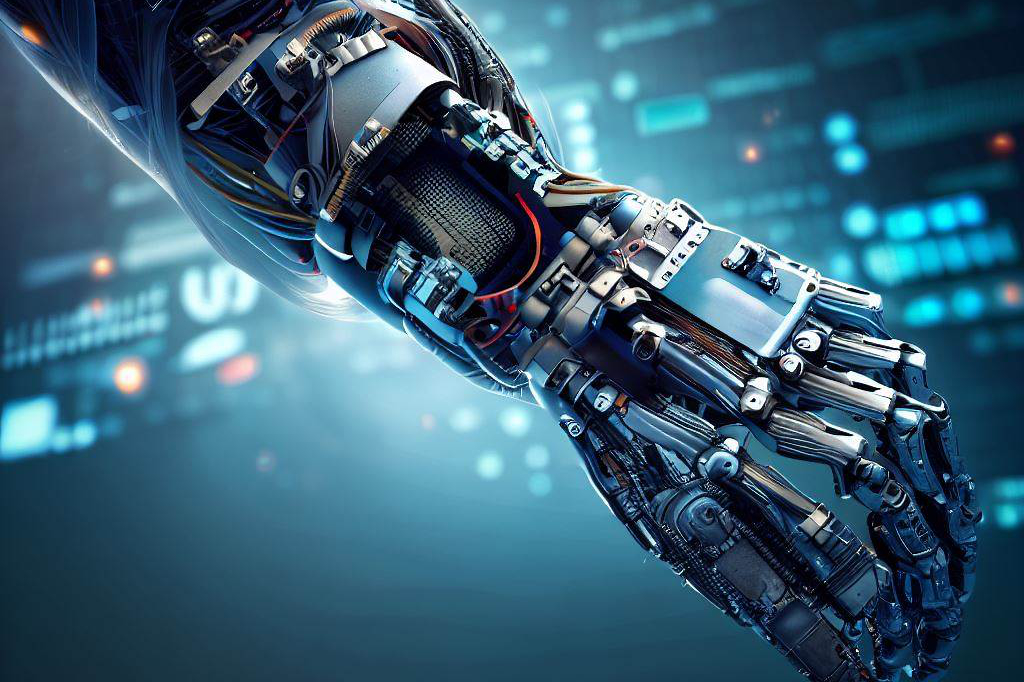
One key development that has made bionic limbs possible is the miniaturization of electronic components. Today’s bionic limbs use compact microprocessors and wireless sensors placed within the limb itself or within a wearable device such as a bracelet or sleeve.
These components work together to detect nerve signals from the brain or muscle movements near the amputation site, which then trigger motor activity within the limb. Another important advance is in myoelectric technology.
Myoelectric prostheses use electrodes placed on the skin near muscle groups to detect electrical signals generated by muscle contractions. These signals can be translated into control commands for a prosthetic limb via software algorithms.
Benefits and Limitations of Bionic Limbs Compared to Traditional Prosthetics
Bionic limbs offer several advantages over traditional prostheses. Firstly, they offer greater functionality by providing more precise control over movement compared to mechanical joints used in traditional prostheses. This means that users can perform complex tasks such as playing musical instruments or typing on a keyboard with greater ease.
Bionic limbs also provide a more natural appearance, as they can be made to match the skin tone and shape of the remaining limb. This means that users can feel more confident in their appearance and blend in better with society.
However, there are some limitations to bionic limbs. Firstly, they are often more expensive than traditional prostheses due to their advanced design and technology.
Additionally, they require regular maintenance and calibration to ensure proper functioning. Not all amputees are eligible for bionic limbs due to factors such as age or medical conditions.
Sensory Restoration
Definition and Explanation of Sensory Restoration
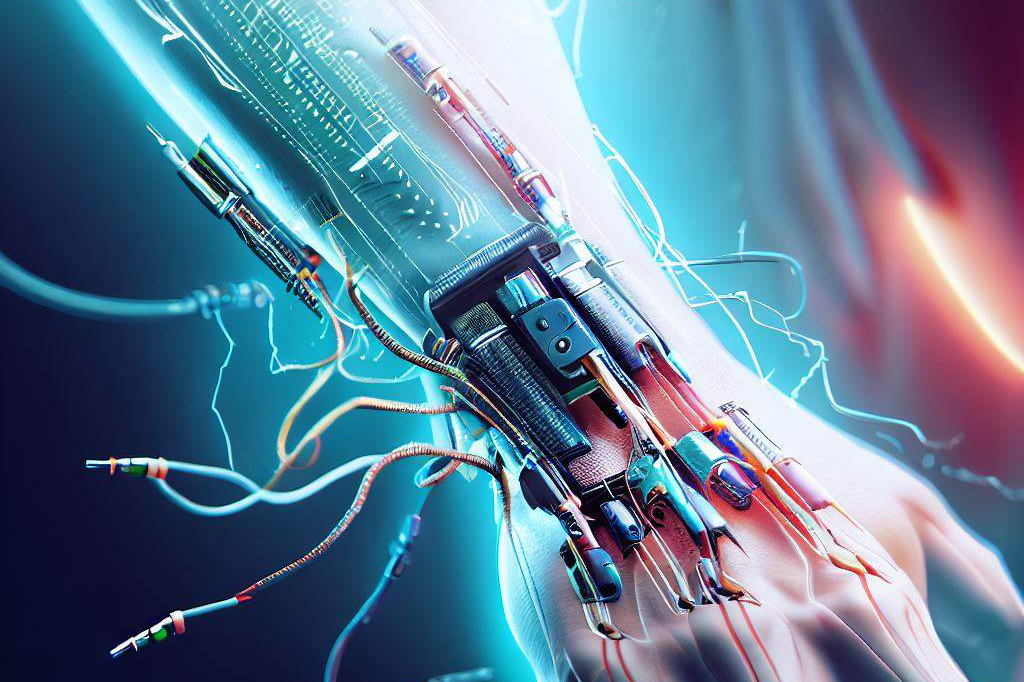
Sensory restoration is the process of restoring the sense of touch to individuals who have lost a limb or suffered from nerve damage. This advancement in prosthetic technology has the potential to greatly improve the quality of life for amputees by allowing them to feel sensations through their prosthetic limbs.
The goal of sensory restoration is to provide amputees with a more natural and intuitive experience when using their prosthetic limb, which can help them perform daily tasks with greater ease and accuracy. One approach to sensory restoration involves implanting electrodes directly into the nerves that would normally carry information from the missing limb.
These electrodes are then connected to sensors on the surface of the prosthetic limb, which are capable of detecting changes in pressure or temperature. When these sensors detect a change, they send electrical signals back to the implanted electrodes, which stimulate the nerves and create a sensation that feels like it is coming from the missing limb.
Current Research on Restoring Sensation to Amputees
There are several ongoing research projects focused on developing new methods for restoring sensation to amputees. One such project involves using virtual reality technology combined with electrical stimulation to create an immersive experience that mimics the sensations of a missing hand or arm. Participants wear a VR headset that displays an image of their missing limb in front of them, while electrical stimulation is used to create sensations such as pressure or heat on their residual limb.
Another promising area of research involves developing new types of sensors that can be implanted directly into nerves or muscles. These sensors are capable of detecting different types of stimuli, such as changes in temperature or pressure, and converting this information into electrical signals that can be sent back to an external device or directly into a nerve.
Potential Benefits and Challenges of Sensory Restoration
The potential benefits of sensory restoration are numerous. For amputees, it can greatly improve their quality of life by allowing them to feel sensations through their prosthetic limb, which can make it easier to perform daily tasks and interact with the world around them.
It can also reduce the risk of injury, as amputees are able to better detect when they are applying too much force or pressure. However, there are also several challenges that need to be addressed before sensory restoration becomes widely available.
One challenge is determining how much sensory information is necessary for an effective experience. Too little information may not be useful, while too much information could be overwhelming and confusing.
Additionally, there is a concern about the long-term effects of electrical stimulation on nerves and muscles. Overall, while there are still many obstacles to overcome in the development of sensory restoration technology, it presents a promising avenue for improving the lives of amputees and advancing the field of prosthetics as a whole.
The Future of Prosthetics

The future of prosthetic technology is bright, with constant advancements being made in the field. One prediction for the future is that prosthetics will become more personalized and customized to fit each individual’s unique needs. This could be achieved through the use of 3D printing technology, which allows for prosthetics to be created quickly and accurately based on precise measurements of a person’s residual limb.
Additionally, there may be an increase in the use of sensors and artificial intelligence in prosthetics, allowing for greater functionality and control. Another potential advancement in bionic limbs is the development of fully implantable prostheses.
This would involve surgically implanting electrodes directly into a person’s muscles or nerves, allowing for direct communication between the prosthesis and the brain. This type of technology would provide a more natural feeling and movement for users, as they would no longer need to rely on external sensors or controllers.
Potential Advancements in Bionic Limbs
In addition to implantable prostheses, other potential advancements in bionic limbs include enhanced sensory feedback and improved battery life. Sensory feedback refers to the user’s ability to receive tactile sensations from their prosthesis. While current technology can provide some sensory feedback through vibrations or pressure changes, researchers are working towards creating more advanced systems that can simulate touch and temperature sensations.
Improved battery life is also an important area for advancement, as many current bionic limbs require frequent charging throughout the day. One potential solution is the development of self-charging batteries that can generate power through movement or heat generated by the user’s body.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Advanced Prosthetic Technology
As with any new technology, there are ethical considerations surrounding advanced prosthetic technology. One concern is accessibility – will these new advancements only be available to those who can afford them?
It’s important that these technologies are accessible to everyone who needs them, regardless of their financial situation. Another consideration is the potential for misuse or abuse of the technology.
For example, could someone use a prosthetic limb as a weapon? As with any powerful tool, it’s important to consider how it could be used for both good and bad purposes.
Overall, while there are certainly ethical considerations surrounding advanced prosthetic technology, the potential benefits to those with limb loss or impairment are immense. With continued research and development, we can create prosthetics that not only restore function but also provide a more natural feeling and movement for users.
Final Thoughts
On the Future of Prosthetics
As we look towards the future of prosthetics, it is clear that remarkable breakthroughs are on the horizon. The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning will provide further advancements in functionality and control over bionic limbs. Meanwhile, advances in robotics will enable researchers to develop new techniques for sensory restoration.
The future of prosthetics holds great promise for individuals with limb loss or impairment. What was once a mere dream may soon become reality as technology continuously improves.
While challenges remain regarding cost-effectiveness and accessibility for both bionic limbs and sensory restoration devices, ongoing research provides hope that these obstacles will be overcome. Overall, as experts continue to push boundaries with new technological advancements in bionics and sensory restoration devices, there is no doubt that the future looks bright for those living with limb loss or impairment.
FAQs
1. What is the history of prosthetics?
– Prosthetics have a long history that dates back to ancient times, with the earliest known prosthetic found in Egypt around 1000 BC. It was an artificial toe made of wood and leather.-
Prosthetics have evolved significantly over time, especially during World War II when there was an increase in demand for limb replacements due to amputations on the battlefield.
– Different materials have been used throughout history, from wood to metal, and more recently, carbon fiber, which provides strength and flexibility.
2. What is the importance of prosthetics?
– Prosthetics play a crucial role in improving the quality of life for people who have suffered limb loss or impairment.
– They help restore normal movement patterns, allow individuals to perform daily activities independently, and even participate in sports or other physical activities.
– For children with limb differences, prosthetics provide opportunities for play and exploration, enhancing their engagement with peers.
– Prosthetics also help prevent secondary health complications that may arise from relying on non-prosthetic aids like crutches or wheelchairs.
3. What are bionic limbs and how do they work?
– Bionic limbs are prosthetic devices designed to replicate the function and appearance of natural limbs.
– Unlike traditional prosthetics, bionic limbs integrate advanced microprocessors, sensors, and motors that enable them to mimic the movement and control of a real limb.
– These limbs use compact microprocessors and wireless sensors to detect nerve signals or muscle movements near the amputation site, which then trigger motor activity within the limb.
4. What are the benefits of bionic limbs compared to traditional prosthetics?
– Bionic limbs offer greater functionality and more precise control over movement compared to mechanical joints used in traditional prosthetics.
– They provide a more natural appearance, as they can be made to match the skin tone and shape of the remaining limb.
– Bionic limbs allow users to perform complex tasks with greater ease, such as playing musical instruments or typing on a keyboard.-
However, bionic limbs can be more expensive than traditional prosthetics and require regular maintenance and calibration.
5. What is sensory restoration and how does it work?
– Sensory restoration is the process of restoring the sense of touch to individuals who have lost a limb or suffered from nerve damage.
– It involves implanting electrodes directly into the nerves that would normally carry information from the missing limb.
– These electrodes are connected to sensors on the surface of the prosthetic limb, which detect changes in pressure or temperature.
– When the sensors detect a change, they send electrical signals back to the implanted electrodes, creating a sensation that feels like it is coming from the missing limb.
These FAQs provide an overview of the history, importance, and advancements in prosthetics, including bionic limbs and sensory restoration. They address common questions and highlight the benefits and limitations of these technologies.
TL;DR…
– 📜 Prosthetics have a long history, dating back to ancient times, with advancements made during World War II.
– 🌱 Prosthetics play a crucial role in improving the quality of life for people with limb loss or impairment.
– 🦾 Bionic limbs replicate the function and appearance of natural limbs using advanced technology.
– ⚙️ Bionic limbs use microprocessors, sensors, and motors to mimic movement and control.
– 👍 Bionic limbs offer greater functionality, a more natural appearance, and improved control compared to traditional prosthetics.
– ⏩ Sensory restoration aims to restore the sense of touch to amputees using implanted electrodes and sensors.
– 🌟 Sensory restoration can greatly improve daily tasks and reduce the risk of injury for amputees.
– 🧠 Ongoing research focuses on virtual reality and electrical stimulation for sensory restoration.
– 💡 The future of prosthetics includes personalized and customized designs, 3D printing, and advanced sensors and AI.
– 🔬 Advancements in bionic limbs may include enhanced sensory feedback and improved battery life.
– 🌍 Ethical considerations include accessibility and potential misuse of advanced prosthetic technology.

C M, a seasoned editor, journalist, and consultant, is deeply fascinated by the convergence of technology, space, and the future of humanity.
With a particular interest in transhumanism, futurology, and the philosophical and ethical dimensions of these domains, C M serves as the lead contributor to TranscendSphere and SpaceSpotlight.
When not penning insightful articles on these rapidly evolving fields, C M indulges in their love for podcasts and books, proudly embracing their status as a ‘Happy Nerd Extraordinaire!’





